| Goals: |
 |
Illustrate building ethane with staggered (D3d ) and
eclipsed (D3h ) symmetries. |
| |
 |
Demonstrate Find Symmetry - Find Irreducible
Fragment - Assign Symmetry - Generate
Ghosts in the Symmetry Toolkit. |
|
Prerequisites: You are familiar with starting the Builder, adding atoms
in the work area, applying
force field clean, and using the
measurement tools.
Setup for Display: Launch the Builder from the Ecce Gateway. To approximate
the screen displays in this example, set the general display style as follows:
- Display menu, Style (All) > Ball & Wireframe
- Display menu, Render as > Normal
- Options menu, Autonormalize Display.
For contrast in this example, the display color of carbon was changed from
default gray to blue.
| In the Builder |
| a. |
Create an ethane molecule in the Builder. |
| b. |
 Clean the ethane molecule using the force field clean function.
Clean the ethane molecule using the force field clean function. |
|
 |
If the Cartesian axes are not displayed, open the View
menu and select Axes. |
| a. |
From the Toolkits menu,
choose Symmetry Toolkit to open the Symmetry Toolkit. |
| b. |
 Click
on the Find Symmetry button. Click
on the Find Symmetry button. |
|
 |
Ecce should determine that symmetry group is D3D and orient the molecule
along the Z axis to show the staggered orientation. D3D should be displayed
in the Symmetry field of the Builder window. |
| - |

Click on the Find Irreducible Fragment button in the Symmetry
Toolkit to generate the symmetry unique set of atoms. |
| |
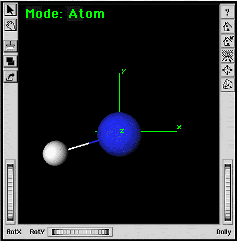 |
A single carbon atom and a single hydrogen atom should be all that remains. |
| a. |
 Click on the Generate Molecule button to create the full
ethane molecule.
Click on the Generate Molecule button to create the full
ethane molecule. |
|
 |
The hydrogen atoms should now be in the eclipsed orientation instead of
the staggered orientation. |
| b. |
 Remove the ghost atoms by clicking on the Clear All
Ghost Atoms button in
the Builder.
Remove the ghost atoms by clicking on the Clear All
Ghost Atoms button in
the Builder. |
|
 |
The hydrogen atoms should now be in the eclipsed orientation instead of
the staggered orientation. |
Ecce Online Help
Revised: April 27, 2004
|
Disclaimer |









